atmospheric pressure → atmosferski tlak
Atmospheric pressure is the pressure exerted by weight of the air above it at any point on the earth’s surface. At sea level the atmosphere will support a column of mercury about 760 mm high. This decreases with increasing altitude. The standard value for the atmospheric pressure at sea level in SI units is 101 325 Pa.
atom marking → markiranje atoma
Atom marking is a process of infusing radioactive isotopes in live organism, with the purpose of revealing a way, diffusion, or a role of certain substance.
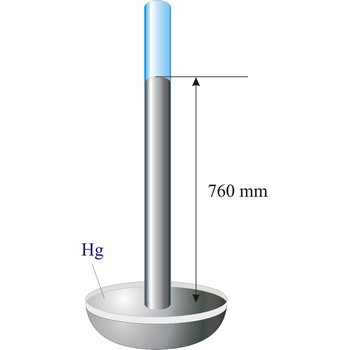
barometer → barometar
Barometer is an instrument that measures atmospheric pressure. A mercury barometer is a closed tube filled with mercury inverted in a mercury reservoir. The height of the mercury column indicates atmospheric pressure (with 1 atm = 760 mm of mercury). An aneroid barometer consists of an evacuated container with a flexible wall. When atmospheric pressure changes, the wall flexes and moves a pointer which indicates the changing pressure on a scale.
basic Bessemer process → bazni Bessemerov proces
Basic Bessemer process is the process of steelmaking in a way that steel, melted iron and limestone are put in the blast-furnace after which the metal oxygen is released in gushes in order to oxidise the impurities.
biochemistry → biokemija
Biochemistry is the study of the chemistry of living organisms, especially the structure and function of their chemical components (principally proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids).
bioelement → bioelement
Bioelement is any chemical element that is found in the molecules and compounds that make up living organism.
Bordeaux mixture → bordoška juha
Bordeaux mixture is a mixture of copper(II) sulphate and calcium hydroxide in water, used as fungicide.
Californian soup → kalifornijska juha
Californian soup is a fungicide and insecticide chemical used for protection of plants, manufactured by boiling sulphur with slaked lime.
carbon dating → određivanje starosti radioaktivnim ugljikom
Carbon dating is used to the time passed since a living organism died. It is based on measuring the quantity of isotope of carbon-14 that is contained in all living organisms.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "živo vapno." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table