ionisation → ionizacija
Ionisation is the process of producing ions. Certain molecules ionise in a solution; for example, acids ionise when dissolved in water.
Electron transfer also causes ionisation in certain reactions, for example sodium and chlorine react by transfer of a valence electron from the sodium atom to the chlorine atom to form the ions that constitute a sodium chloride crystal.
iridium → iridij
Iridium was discovered by Smithson Tennant (England) in 1803. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word iris, meaning rainbow, because its salts are highly colored. It is heavy, brittle, white metal. Unreactive in air, water and acids. Attacked by fused NaOH. Metal ignites and burns readily. Iridium is found in gravel deposits with platinum. Used with osmium to tip gold pen points, to make crucible and special containers. Also to make alloys used for standard weights and measures and heat-resistant alloys. Also as hardening agent for platinum.
weak acid → slaba kiselina
Weak acid is an acid that incompletely dissociated in aqueous solution. Acetic acid is an example of a weak acid
weak base → slaba baza
Weak base is a base that only partially dissociates into ions in solution. Weak bases are weak electrolytes. Ammonia is an example of a weak base
weak electrolyte → slabi elektrolit
Weak electrolytes are those electrolytes which in water solutions dissociate only partially, giving ions and which are in equilibrium with undissociated molecules. Their water solutions conduct electric current weakly. For example, acetic acid partially dissociates into acetate ions and hydrogen ions, so that an acetic acid solution contains both molecules and ions.
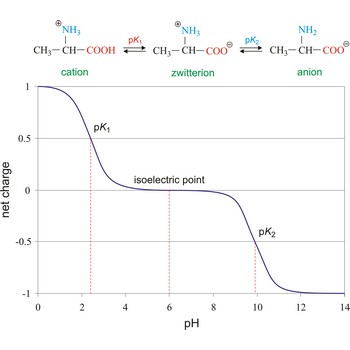
isoelectric point → izoelektrična točka
Isoelectric point (pI or IEP) is the pH of a solution or dispersion at which the net charge on the molecules or colloidal particles is zero. In electrophoresis there is no motion of the particles in an electric field at the isoelectric point. The net charge (the algebraic sum of all the charged groups present) of any amino acid, peptide or protein, will depend upon the pH of the surrounding aqueous environment. For example, alanine can have a charge of +1, 0, or -1, depending on the pH of the solution in which it is dissolved.
kinetic energy → kinetička energija
Kinetic energy (Ek) is associated with the state of motion of a body. It is a scalar property and defined to be
Kinetic energy is most clearly exhibited in gases, in which molecules have much greater freedom of motion than in liquids and solids.
Kjeldahl’s method → Kjeldahlov postupak
Kjeldahl’s method is an analytical method for determination of nitrogen in certain organic compounds. The method was developed by the Danish chemist Johan Kjeldahl (1849-1900).
It involves addition of a small amount of anhydrous potassium sulphate to the test compound, followed by heating the mixture with concentrated sulphuric acid, often with a catalyst such as copper sulphate. As a result ammonia is formed. After alkalyzing the mixture with sodium hydroxyde, the ammonia is separated by distillation, collected in standard acid, and the nitrogen determined by back-titration.
- Kjeldahl flask for decomposition (500 ml – macro or 100 ml - micro)
- funnel for alkaline solution
- Wagner tube (drop catcher)
- condenser
- absorption flask with known volume of standard acid
X-ray diffraction pattern → rendgenski difrakcijski uzorci
X-ray diffraction pattern is an interference pattern created by x-rays as they pass through a solid material. Studying X-ray diffraction patterns gives detailed information on the three-dimensional structure of crystals, surfaces, and atoms.
zeta potential → zeta potencijal
Zeta potential (ζ) is the potential across the interface of all solids and liquids. Specifically, the potential across the diffuse layer of ions surrounding a charged colloidal particle, which is largely responsible for colloidal stability. Also called electrokinetic potential.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "čvrste otopine." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table