Results 1–3 of 3 for Ostwald’s+viscometer
Ostwald’s viscometer → Ostwaldov viskozimetar
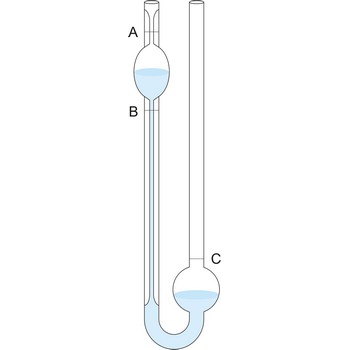
Ostwald viscometer, also known as U-tube viscometer or capillary viscometer is a device used to measure the viscosity of the liquid with a known density. The method of determining viscosity with this instrument consists of measuring the time for a known volume of the liquid (the volume contained between the marks A and B) to flow through the capillary under the influence of gravity. Ostwald viscometers named after the German chemist Wilhelm Ostwald (1853-1932).
The instrument must first be calibrated with materials of known viscosity such as pure (deionized) water. Knowing the value of viscosity of one liquid, one can calculate the viscosity of other liquid.
where η1 and η2 are viscosity coefficients of the liquid and water, and ρ1 and ρ2 are the densities of liquid and water, respectively.
Ostwald’s dilution law → Ostwaldov zakon razrjeđenja
Ostwald’s dilution law is a relation for the concentration dependence of the molar conductivity Λ of an electrolyte solution, viz.
where c is the solute concentration, Kc is the equilibrium constant for dissociation of the solute, and L0 is the conductivity at cΛ = 0. The law was first put forward by the German chemist Wilhelm Ostwald (1853-1932).
Ostwald’s process → Ostwaldov proces
Ostwald’s process is a process by which the nitric acid can be obtained in three degrees. In the first stage ammonia and oxygen react (with platinum-rhodium as a catalyst), whereby the nitrogen monoxide and water emerge
In the second stage nitrogen monoxide reacts with oxygen whereby nitrogen dioxide emerges
and in the third stage nitrogen dioxide dissolves in water, in the presence of air, giving the nitric acid
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ostwald’s+viscometer." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table