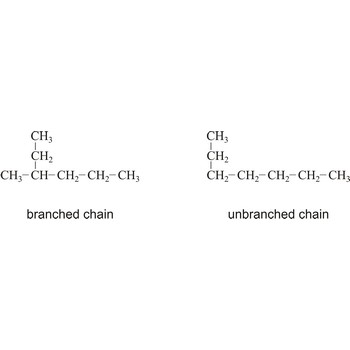
branched chain → razgranati lanac
Branched chain is an open chain of atoms with one or more side chains attached to it.
lateral chain → postranični lanac
Lateral chain is a shorter chain of hydrocarbons which is connected to the main chain of hydrocarbon.
chain → lanac
Chain is a linear combination of the same type of atom in a molecule. In straight chain molecules, the atoms are arranged in a line, with each atom in the chain linked to one preceding atom and one succeeding atom of the same type. A closed chain molecule is a chain where the atoms are linked in a ring structure.
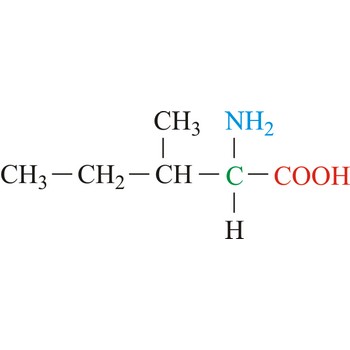
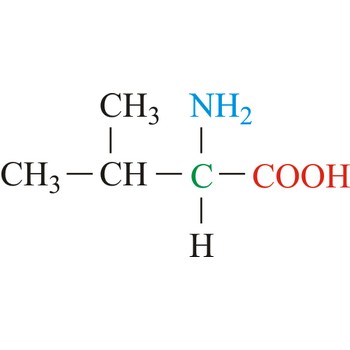
isoleucine → izoleucin
Isoleucine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is one of the three amino acids having branched hydrocarbon side chains. The side chains of these amino acids are not reactive but, these residues are critically important for ligand binding to proteins, and play central roles in protein stability. Isoleucine is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Ile, I
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C6H13NO2
- Molecular weight: 131.12 g/mol
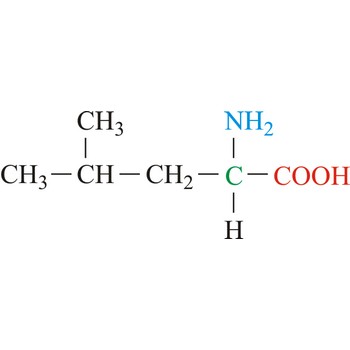
leucine → leucin
Leucine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It has one additional methylene group in its side chain compared with valine. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Leucine is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Leu, L
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C6H13NO2
- Molecular weight: 131.17 g/mol
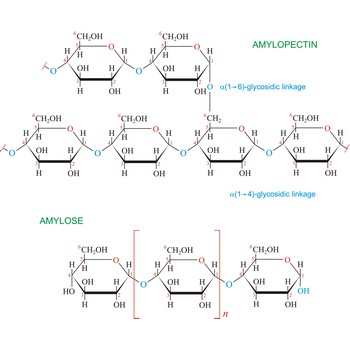
starch → škrob
Starch (C6H10O5)x is a polysaccharide used by plants to stockpile glucose molecules. It is the major component of flour, potatoes, rice, beans, corn, and peas. Starch is a mixture of two different polysaccharides: amylose (about 20 %), which is insoluble in cold water, and amylopectin (about 80 %), which is soluble in cold water. Amylose is composed of unbranched chains of D-glucose units joined by α(1→4)-glycosidic linkages. Unlike amylose, which are linear polymers, amylopectin contains α(1→6)-glycoside branches approximately every 25 glucose units.
Starch digestion begins in the mouth via the action of amylase, a digestive enzyme present in saliva. The process is completed in the small intestine by the pancreatic amylase. The final products of starch digestion, glucose molecules, are absorbed into the intestinal bloodstream and transported to the liver. Like most enzymes, glycosidases are highly selective in their action. They hydrolyze only the α-glycoside links in starch and leave the β-glycoside links in cellulose untouched. Starch is important food stuff and is used in adhesives, and sizes, in laundering, pharmacy and medicine.
valine → valin
Valine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is a member of the branched-chain amino acid family, along with leucine and isoleucine. Valine differs from threonine by replacement of the hydroxyl group with a methyl substituent, but they are of roughly the same shape and volume. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Valine is an essential amino acid, which means that it cannot be synthesized in the body and must be obtained through dietary sources.
- Abbreviations: Val, V
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-methylbutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H11NO2
- Molecular weight: 117.15 g/mol
alkanes → alkani
Alkanes (paraffins) are acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having the general formula CnH2n+2, and therefore consisting entirely of hydrogen atoms and saturated carbon atoms. In the systematic chemical nomenclature alkane names end in the suffix -ane. They form a homologous series (the alkane series) methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10), etc. The lower members of the series are gases; the high-molecular mass alkanes are waxy solid. Generaly the alkanes are fairly unreactive. They form haloalkanes with halogens when irradiated with ultraviolet radiation. Alkanes are present in natural gas and petroleum.
alkenes → alkeni
Alkenes are acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having one or more double carbon-carbon bonds in their molecules. In the systematic chemical nomenclature, alkene names end in the suffix -ene. The general formula is CnH(2n+2)-2x were x is the number of double bonds. Alkenes that have only one double bond form a homologous series: ethene (ethylene), CH2=CH2, propene, CH3CH2=CH2, etc. Alkenes typically undergo addition reactions to the double bond.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Razgranati lanac." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table