Results 1–3 of 3 for alanin
alanine → alanin
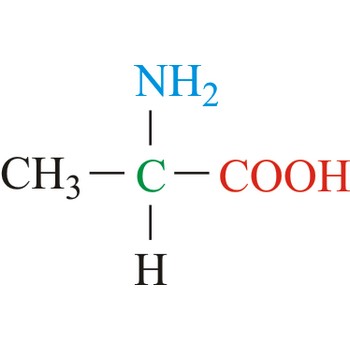
Alanine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is the second simplest amino acid, but used the most in proteins. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Alanine is a nonessential amino acid, meaning it can be manufactured by the human body, and does not need to be obtained directly through the diet.
- Abbreviations: Ala, A
- IUPAC name: 2-aminopropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2
- Molecular weight: 89.09 g/mol
isoelectric point → izoelektrična točka
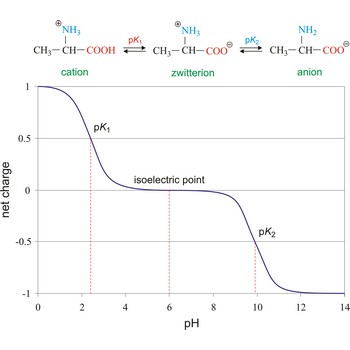
Isoelectric point (pI or IEP) is the pH of a solution or dispersion at which the net charge on the molecules or colloidal particles is zero. In electrophoresis there is no motion of the particles in an electric field at the isoelectric point. The net charge (the algebraic sum of all the charged groups present) of any amino acid, peptide or protein, will depend upon the pH of the surrounding aqueous environment. For example, alanine can have a charge of +1, 0, or -1, depending on the pH of the solution in which it is dissolved.
Dipeptide → Dipeptid
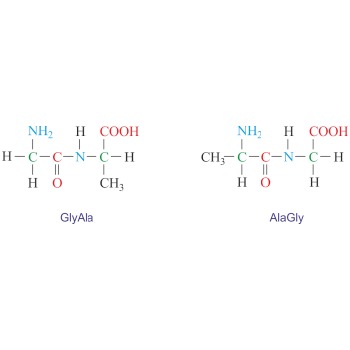
Dipeptide is an organic compound formed when two amino acids are joined by a peptide bond. Depending on which groups of amino acids are involved in the peptide bond four dipeptides can be formed from two different amino acids. For example, glycine (Gly) and alanine (Ala) can give two symmetrical dipeptides (GlyGly and AlaAla) and two unsymmetrical dipeptides (GlyAla and AlaGly). The naming is done by reading the sequence from the N-terminus to the C-terminus.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Alanin." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table