Earth’s crust → Zemljina kora
Crust is outer layer of the solid earth, above the Mohorovicic discontinuity. Its thickness averages about 35 km on the continents and about 7 km below the ocean floor, and has the approximate chemical composition:
| Element | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| oxygen | 47 |
| silicon | 28 |
| aluminium | 8 |
| iron | 4.5 |
| calcium | 3.5 |
| sodium | 2.5 |
| potassium | 2.5 |
| magnesium | 2.2 |
alkaline earth metal → zemnoalkalijski metal
Alkali earth metal is a term that refers to six elements: beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). These elements make up group 2 of the periodic table of elements. They all exhibit a single oxidation state, +2. They are all light and very reactive. Barium and radium are the most reactive and beryllium is the least.
To denote slightly soluble metal oxides chemists formerly used the term "earth". The oxides of barium, strontium, and calcium resemble alumina (Al2O3), a typical "earth", but form alkaline mixtures with water. For this reason barium, strontium, and calcium were called alkaline earth metals. This name has now been extended to include all of the elements of group 2.
diatomaceous earth → dijatomejska zemlja
Diatomaceous earth is a naturally occurring siliceous sedimentary mineral compound from microscopic skeletal remains (frustules) of diatoms, unicellular aquatic plants of microscopic size. Their fossilized remains are called diatomite and contains approximately 3000 diatom frustules per cubic millimetre.
Diatomite is relatively inert and has a high absorptive capacity, large surface area, and low bulk density. It consists of approximately 90 % silica, and the remainder consists of compounds such as aluminum and iron oxides. The fine pores in the diatom frustules make diatomite an excellent filtering material for waters, beverages, oils, chemicals, as well as many other products.
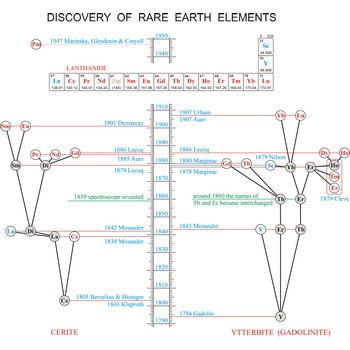
rare earth elements → elementi rijetkih zemalja
Rare earth elements (metals) are the elements scandium (Sc), yttrium (Y), and the lanthanides (La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu). These elements got their name from the fact that chemists first isolated them in their oxide forms. These oxides somewhat resemble calcium, magnesium and aluminium oxides, sometimes called common earths. Do you want to know more?
abundance of elements → rasprostranjenost elemenata
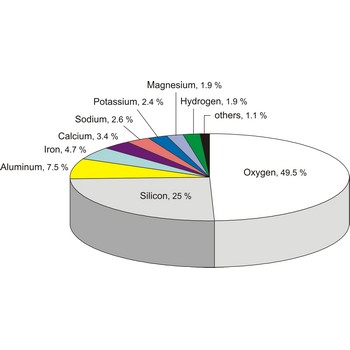
Elements in nature are mostly found in different compounds and, rarely, in the free (elementary) state. In Earth’s crust the most abundant of all elements is oxygen (with 49.5 %), then silicon (25 %), aluminium (7.5 %), iron (4.7 %), calcium (3.4 %), sodium (2.6 %), potassium (2.4 %), magnesium (1.9 %) and hydrogen (1.9 %). These nine elements make up almost 99 % of the Earth’s composition.
abundance of substances → rasprostranjenost tvari
Abundance of substances is the ratio of the total mass of a specified element in the Earth’s crust to the total mass of the Earth’s crust. It is often expressed as a percentage.
aluminium → aluminij
Aluminium was discovered by Friedrich Wöhler (Germany) in 1827. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word alumen meaning alum. It is soft, lightweight, silvery-white metal. Exposed surfaces quickly form protective oxide coating. Metal reacts violently with oxidants. Third most abundant element in the earth’s crust. Aluminium is the most abundant metal to be found in the earth’s crust, but is never found free in nature. Aluminium is obtained by electrolysis from bauxite. Used for many purposes from airplanes to beverage cans. Too soft in its pure form so less than 1 % of silicon or iron is added, which hardens and strengthens it.
iron → željezo
Iron has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word ferrum meaning iron. It is malleable, ductile, silvery-white metal. Exposed surfaces form red-brown oxides. Forms very strong alloys (steel). Ferromagnetic. Metal dust flammable. Fourth most abundant element in the earth’s crust. Iron is obtained from iron ores. Pure metal produced in blast furnaces by layering limestone, coke and iron ore and forcing hot gasses into the bottom. This heats the coke red hot and the iron is reduced from its oxides and liquefied where it flows to the bottom. Iron is the most common metal in human society. More than 90 % of all metal refined in the world is iron. Used in steel and other alloys. It is the chief constituent of hemoglobin which carries oxygen in blood vessels. Its oxides are used in magnetic tapes and disks.
lithosphere → litosfera
Lithosphere (from the Greek for rocky sphere) is rigid, rocky outer layer of the Earth, consisting of the crust and the solid outermost layer of the upper mantle. The distinguishing characteristic of the lithosphere is not its composition but its flow properties. It floats on the asthenosphere, which is the heat-softened layer of the mantle below the lithosphere.
The lithospheric is not one continuous piece but is broken into about a dozen major separate rigid blocks, or plates, which move independently relative to one another. This movement of lithospheric plates over the asthenosphere is described as plate tectonics. When an oceanic plate and a continental plate meet, the heavier oceanic plate (composed mostly of basalt, specific gravity about 3.0 or peridotite, specific gravity about 3.3) subducts under the lighter continental plate (composed mostly of granite, specific gravity about 2.7).
oxygen → kisik
Oxygen was discovered by Joseph Priestley (England) in 1774. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words oxy genes meaning acid and forming (acid former). It is colourless, odourless gas; pale blue liquid. Extremely reactive. Forms oxides with nearly all other elements except noble gases. It is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust and makes up almost 21 % of the atmosphere. Oxygen is obtained primarily from liquid air by fractional distillation. Small amounts are made in the laboratory by electrolysis of water. Used in steel making, welding and supporting life. Naturally occurring ozone (O3) in the upper atmosphere shields the earth from ultraviolet radiation.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Earth’s crust." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table