atom marking → markiranje atoma
Atom marking is a process of infusing radioactive isotopes in live organism, with the purpose of revealing a way, diffusion, or a role of certain substance.
atom → atom
Atom is an atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of the element. Rutherford-Bohr’s model represents the atom as a positively charged core of a size around 10-14 m composed of protons (positive particles) and neutrons (neutral particles) around which negatively charged electrons circle. The number of protons and electrons are equal, so the atom is an electrically a neutral particle. Diameter of the atom is about 10-10 m.
atom radius → radijus atoma
Atoms and molecules have no strict boundaries. The volume of a free atom is usually defined as that volume that contains 90 % of electron cloud. The radius of an atom represents half of interatom distance of two identical atoms which are in touch but are not interconnected either by a covalent or an ionic bond, but with a very weak van der Waals’s bond.
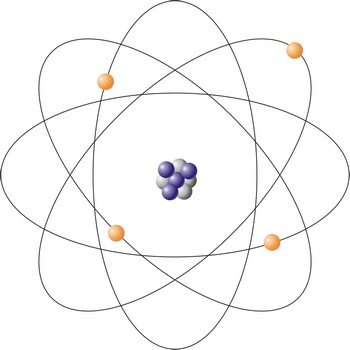
Bohr atom → Bohrov atom
Bohr atom is a model of the atom that explains emission and absorption of radiation as transitions between stationary electronic states in which the electron orbits the nucleus at a definite distance. The Bohr model violates the Heisenberg uncertainty principle since it postulates definite paths and moment for electrons as they move around the nucleus. Modern theories usually use atomic orbitals to describe the behaviour of electrons in atoms.
percentage composition of atom in the molecule → postotni sastav atoma u molekuli
Percentage composition of atom in the molecule is a structure of compound presented in the shape of a percentage of its mass, which comes from every element.
atomic absorption spectroscopy → atomska apsorpcijska spektroskopija
Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) An analytical technique in which a sample is vapourised and the nonexcited atoms absorb electromagnetic radiation at characteristic wavelengths.
atomic clock → atomski sat
Atomic clock is an apparatus for standardizing time based on periodic phenomena within atoms or molecules (ammonia clock; caesium clock).
atomic number → atomski broj
Atomic number (Z) is a characteristic property of an element, equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. The atomic number and the element symbol are two alternate ways to label an element. In nuclide symbols, the atomic number is a leading subscript; for example, in 2He.
atomic orbital → atomska orbitala
Atomic orbital is a wave function that describes the behaviour of an electron in an atom.
atomic spectroscopy → atomska spektroskopija
Atomic spectroscopy is an expensive analytical method which uses absorption (AAS), emission (AES) and fluorescent (AFS) characteristics of the analyte.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Bohrov atom." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table